Axon Misguidance
During development axon growth can be misdirected due to various mistakes that can arise in the sginal machinery. An example of this may be localisation of repulsive molecules in potential axon tract. This may be an impediment to axon growth creating a different path. Several disorders result from errors in axon guidance. Genetic disorders include Corpus Callosum Dysgenesis, Duane Retraction Syndrome, L1 syndrome, Albinism and many more.
Corpus Callosum Dysgenesis
This is a disorder that sees erroneous midline crossing, and results in mental retardation raging in severity. The corpus callosum is responsible for connecting homologous cortical regions of left and right brain hemisphers. In corpus callosum dysgenesis defects in developmental process such as cell proliferation and axon growth and guidance may result in axons failing to cross the midline. These axons may inturn form longitudinally orientated bundles located medially to lateral ventricles. This orientation can serve as an indicator of axon misguidance.

Orignal image courtesy of https://www.flickr.com/photos/reighleblanc/3854684694/sizes/s/in/photostream
L1 Syndrome
L1 syndrome is an x- linked neurological disorder that results from mutations in the L1CAM gene. It was recognised as four distinct entities (x-linked hydrocephalus, MASA, x-linked complicated spastic paraplegia and x-linked corpus callosum agenisis.) These are now all categorised as one class of disease. The L1CAM gene encodes the L1 transmembrane neural adhesion molecule. This acts as a short range guidance cue and is highly expressed in neuronal developing areas. Mutations in the L1CAM gene may be missense, nonsense, frameshift and splice site mutations.
Duane Retraction Syndrome
DRS is a disorder that affects 1:1000 individuals. Symptoms include restricted horizontal gaze and occular synkinesis. Individuals with the autosomal dominant form of DRS have mutations in CHN1(a DRS gene). Mutations in this gene show higher incednces of vertical movemnt abnormalities. The pathway involves the formation or alteration of signalling proteins that help transduce axon guidence.
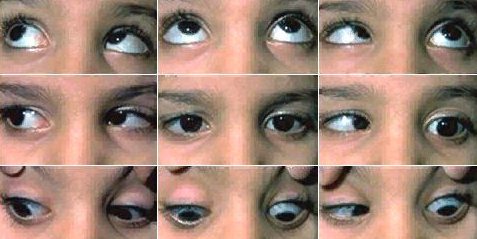
Image courtesy of https://webeye.ophth.uiowa.edu/eyeforum/cases/56-Duanes-Retraction-Syndrome.htm
Kallmann Syndrome
Congenital anosmia (lack of sense of smell), hypogonadotropic hypogonadism are characteristic of this syndrome. Defects in the hypothalamic release of gonadotropin releasing hormone, results in the condusive loss in hypophoseal release of sex hormones causing a failure to reach sexual maturation. KAL1 Gene that encodes glycoprotien anosimin-1 is thought to be involved in cell adhesion, neurite outgrowth and axon guidence activites. Mutations in this gene may be responsible for changes seen in this syndrome.
